What Gas Law Best Describes Respiration
K 1 pV. This empirical law was observed by John Dalton in 1801 and is related.
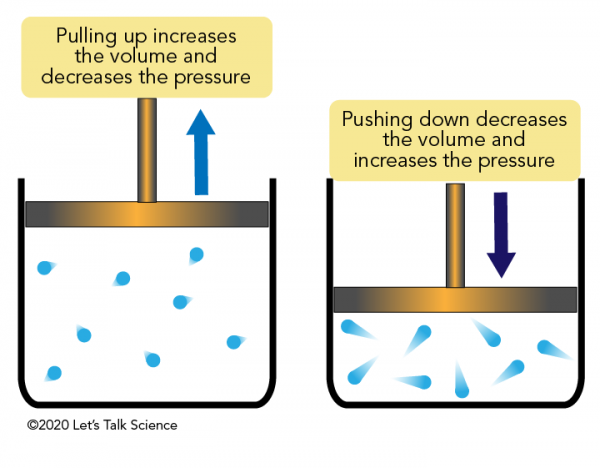
Boyle S Law Let S Talk Science
According to Boyles law if a given amount of gas has a constant temperature increasing its volume decreases its pressure and vice-versa.

. Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules 6023 10 23 Avogadros number. This causes air to flow into the lungs from high pressure to low pressure. Exhalation can be accomplished by just relaxing the chest and allowing the elastic recoil of the alveoli to force the air out of the lungs.
It describes both the bulk flow of air into and out of the lungs and the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide into the bloodstream through diffusion. Universal Ideal Gas Law. On rearranging we get.
Which of the following statements best describes the definition of Daltons Law of partial pressures. - OXYGEN LOWER PRESSURE LOWER amount of oxygen available for gas exchange is less remember BOYLES LAW P 1V lower outside pressure means lungs open up more than normal remember HENRYS LAW more CO_2 coming out of solution in your lungs. By the ideal gas law we know that an expanded volume will lower the pressure and allow air to flow into the lungs through the bronchial passages.
Both equations state that the product of the pressure and volume remains the same. Now if a fixed mass of gas undergoes an expansion at constant temperature then the final volume and pressure shall be p 2 and V 2. A number representing the universal gas constant.
The initial volume and initial pressure here is p 1 and V 1 then according to Boyles law. Boyles law is a gas law that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of gas for a mass and temperature. Daltons law states that.
The volume of gas that will dissolve in a solvent is proportional to the solubility of the gas and the gas pressure. In terms of respiration Charless law is the least applicable since body temperature rarely changes by much. A measurement of the absolute pressure of a gas.
The pressure of any gas is inversely proportional to its volume when at a constant temperature. PV T k. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Using the numbers below calculate the total pressure of the atmosphere. The gas volume and temperature are directly proportional 2. Gas Laws and Breathing.
A measure of the total amount of the gas usually measured in moles. Which of the following best describes the affect this has on gas exchange. External respiration is the formal term for gas exchange.
Daltons law states that the total pressure exerted by the mixture of inert non-reactive gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of individual gases in a volume of air. The gas volume and temperature are inversely proportional 3. A measurement of the volume that the gas occupies usually measured in liters.
The increase in volume leads to a decrease in pressure Boyles law. This law is the mechanism by which the human respiratory system functions. The law states that if the volume increases then the pressure must decrease or vice versa.
The combined gas law is also known as a general gas equation is obtained by combining three gas laws which include Charles law Boyles Law and Gay-Lussac law. Every chemistry student learns three basic gas laws. The distance between the alveolar surface and the endothelium in the respiratory membrane increases to a point at which the surfaces are too far away for efficient gas exchange.
Boyles Law describes the relationship between the pressure P and the volume V of a gas. The total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases. DONT GET ENOUGH OXYGE LOSE TOO MUCH CO_2 Altitude Sickness which can be fatal.
While the bulk flow of air from the external environment happens due to pressure changes in the lungs the mechanisms of alveolar gas. This relationship is often written algebraically as PV constant or P 1 V 1 P 2 V 2. Charless law states the given constant pressure as the temperature of the gas increases so does the pressure.
The pressure of gas in your lungs is inversely proportional to the volume in your lungs. The law shows the relationship between temperature volume and pressure for a fixed quantity of gas. The correct answer is 1.
When you inhale muscles increase the size of your thoracic chest cavity and expand your lungs. Respiration is the biochemical process in which the cells of an organism obtain energy by combining oxygen and glucose resulting in the release of carbon dioxide water and ATP the currency of. The state of a fixed mass of gas is determined by its pressure volume and temperaturePV.
External respiration gas exchange that occurs in the alveoli Henrys law statement of the principle that the concentration of gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the solubility and partial pressure of that gas internal respiration gas exchange that occurs at the level of body tissues partial pressure. A value representing the absolute temperature. Charless law Boyles law and Daltons law.
Start studying Gas Laws and the Respiratory System. When you exhale the process reverses. Boyles law is equivalent to PV K P is pressure V is volume K is a constant or one may state that pressure is inversely proportional to the volume1.
Boyles law was derived by Robert Boyle to describe the relationship between volume and pressure of a gas. Daltons Law in Respiration Daltons law states that at any given time the percentage of each of these gasses in the air we breathe makes its contribution to total atmospheric pressure and this contribution will depend. The physiological definition of respiration differs from the biochemical definition which refers to a metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy in the form of ATP and NADPH by oxidizing.
The general equation of combined gas law is given as. Your diaphragm and rib muscles relax your chest cavity contracts and your lung volume decreases causing the pressure to increase Boyles law again and air flows out of the lungs from high. In physiology respiration is the movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells within tissues and the removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction.
We can breathe air in and out of our lungs because of Boyles law.



Belum ada Komentar untuk "What Gas Law Best Describes Respiration"
Posting Komentar